-
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies are the underlying technology that power DeFi. However, to give businesses a more potent infrastructure and support the future of DeFi, industry experts are fusing DeFi and Crypto with Web3 using blockchain development services.
These three technologies are driving significant transformation across the DeFi ecosystem. But cross-chain Defi technology is at the forefront concerning the most recent buzz in the Defi community.
Therefore, let's take a closer look at cross-chain technology and see how it helps the development of the current DeFi infrastructure.
Cross-Chain Interoperability for DeFi Projects
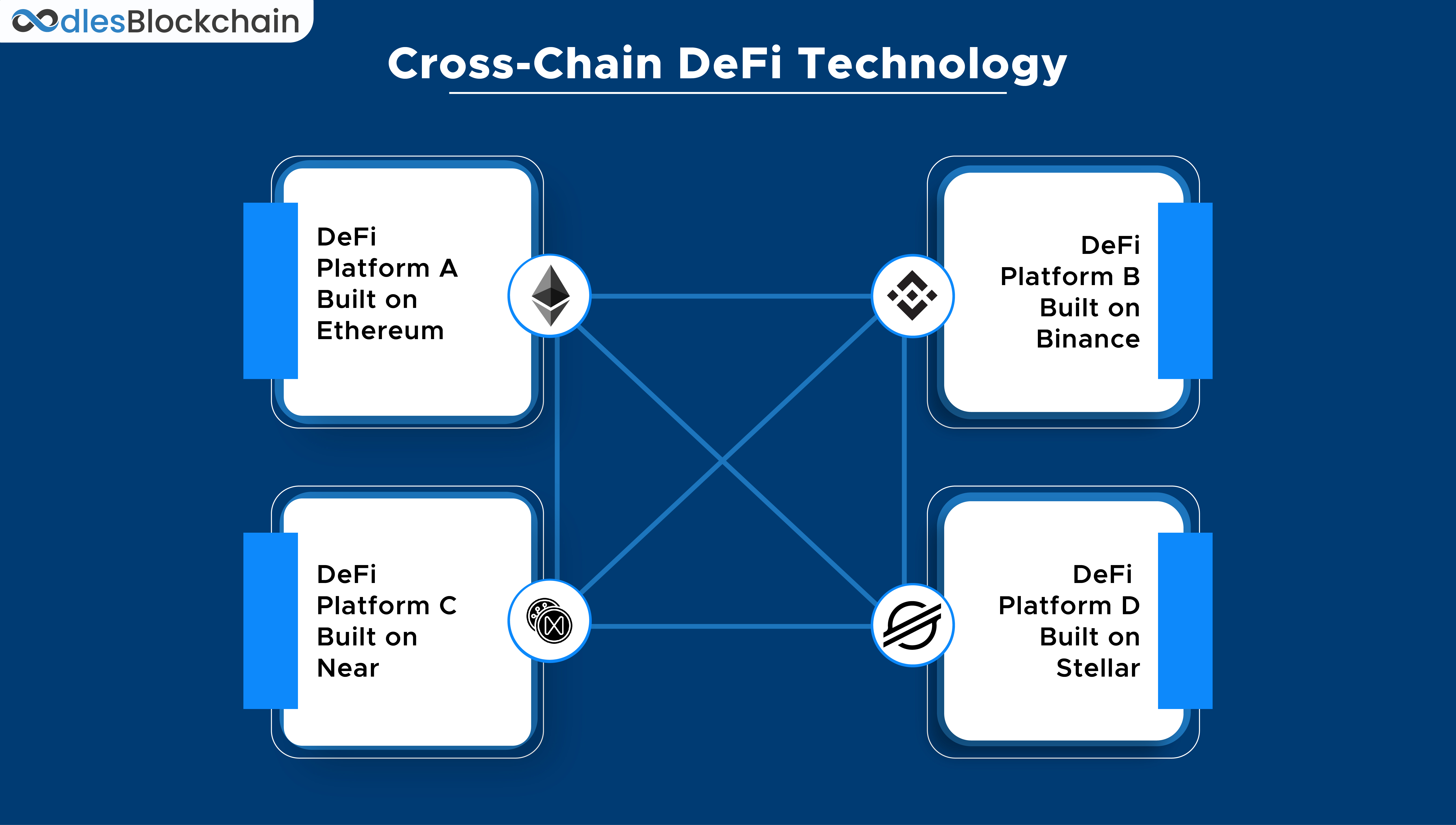
To facilitate information sharing, a blockchain network must be able to communicate with other blockchains that use similar underlying technology.
This is known as cross-chain interoperability. Keep in mind that "cross-chain" is not the same as "multi-chain," which describes a project that runs concurrently across multiple networks.
Theoretically, users may move value seamlessly and securely across different networks via token bridges by using cross-chain bridges and communication channels.
Its interoperability might make it possible for other blockchain networks to communicate with one another, with DeFi standing to gain the most from this.
Also, Visit | Decrypting Fundamentals of DeFi Aggregator Development
How Crucial is Cross-Chain Compatibility in DeFi
DeFi protocols had a restriction on serving the blockchain's crypto community until cross-chain interoperability became possible.
The most well-known blockchain ecosystem did not allow non-Ethereum users to participate in decentralized finance.
DeFi protocols could only operate with the original blockchain they were based on due to a lack of interoperability.
They thereby acquired all the underlying difficulties connected with their native network.
This resulted in sluggish transaction times and high gas costs for Ethereum. Low liquidity and a smaller customer base affected certain others.
Therefore, cross-chain interoperability changed the rules of the decentralized finance game.
Projects no longer need to build exclusively for one network because cross-chain bridges make it simple to transfer digital assets between blockchains.
Additionally, users can always transfer assets between networks, farm new tokens without restrictions, deposit liquidity, collect and repay loans, and perform cross-chain token swaps.
Also, cross-chain compatibility provides access to DeFi for previously marginalized participants, opening doors for both institutional and retail customers.
You May Also Want to Read | Defi Lending and Borrowing Platform Development
Key Differences between Cross-chain and Regular DeFi
Bridges keep demonstrating how important they are to the DeFi ecosystem.
They are advantageous for the entire blockchain ecosystem, not just the end users.
Bridges offer Adaptability
They enable users to move valuable data and assets from one blockchain to another.
Without being constrained by the capabilities of a single chain, users can take advantage of the advantages of several blockchain technologies.
Cross-chain Compliance
Users can take advantage of all the advantages of a specific blockchain by using cross-chain bridges.
One of the most common cases is Solana blockchain users using Ethereum's blockchain's DeFi functionality.
Holders of Solana on Ethereum can trade and profit from the established DeFi ecosystem.
Blockchain-to-Blockchain Interactions
Through a connection between the L1 main chain (parent chain) and the L2 chain, bridges enable interactions across different blockchains (child chain). As a result, developers can integrate and use DApps on DeFi platforms (such as rollups built on Ethereum).
Scalability
DeFi bridges greatly increase blockchain network scalability. This is feasible because a bridge connects the primary and secondary chains, enabling the majority of transactions to take place throughout the ecosystem.
Efficiency
Users can transfer their assets using bridges from a non-scalable blockchain to a high-performance blockchain, taking advantage of reduced gas costs and the strength of Ethereum smart contracts. Even faster microtransactions can be made on-chain without concern for exorbitant fees.
Also, Visit | A Guide to Defi Token Development Like Safemoon
Types of Cross-Chain Bridges
Based on different criteria, such as the types of blockchains they support and the trust mechanisms they use, we can classify cross-chain bridges.
Bridges can be broadly grouped into the following categories based on their characteristics:
Backed chains
The types of blockchains that cross-chain bridges support can also be used to categorize them. The following situations are covered by this classification:
One Asset Moves between Two Chains
To move a certain coin to another chain, there are bridges. You can move BTC from the Bitcoin blockchain to Ethereum using services like wBTC (managed by BitGo) and BTC (managed by Keep Network), for instance.
Moving Various Assets between Two Chains
Several bridges let you transfer multiple tokens, but only between two chains. For instance, the NEAR protocol can receive ETH and other ERC-20 tokens from Ethereum using Rainbow Bridge.
Similar multi-asset transfers between Ethereum and Cosmos and Binance Smart Chain (BSC) are supported by Gravity and ZeroSwap, respectively.
Moving Resources from One Chain to Several Chains
Users can link a chain to several blockchains using certain cross-chain bridges.
A wormhole is one example, which connects Solana assets to Ethereum, Fantom, Avalanche, Terra, and Polygon.
Multiple Asset Transfers between Various Chains
Some cross-chain bridges improve interoperability by making it easier for tokens to transfer between separate blockchains. Such bridges can be incorporated by developers into dApps to boost the liquidity available.
Connect with our skilled blockchain development experts for more information about cross-chain DeFi development.

Our Offices
INDIA
Emaar Digital Greens, Sector 61,
Gurugram, Haryana
122011.
Welldone Tech Park,
Sector 48, Sohna road,
Gurugram, Haryana
122018.
















