-
This post assesses how Hyperledger blockchain development with Indy can solve the identity management problem worldwide. First, let's explore how current centralized identity management functions, and why there's a revolutionary shift is required.
Centralized Identity Management
Usually, a centralized governing body has control of everything related to our identities. It includes the issuance of website security certificates, the curation of offline and online information, the monitoring of access to the world wide web, and more. A centralized model enables authorities to accumulate the personal data of users that might be vulnerable to various risks. Storing sensitive information in centralized models and their monitoring by governing officials expose potential data breaches.
- No transparency
- Identity theft risks
- Disparate identities
- Cost-draining
While the current identity management systems fail to resolve these problems, self-sovereign identity gives all power to identity owners. Also, Explore | Benefits of Digital Identity Management With Blockchain
Self-Sovereign Identity
The concept of self-sovereign decentralized digital identity provides ownership over personal information to owners, instead of third parties or organizations. It proposes the idea that an identity system should be a decentralized network to make an identity self-sovereign. Hyperledger Indy is one of the platforms to develop decentralized identity management systems. Before stepping into the Hyperledger Indy ecosystem for digital self-sovereign identity management, let's understand decentralized identity management in detail.
Decentralized Self-sovereign Identity Management
Assume someone is moving to a new country. It will require them to apply for different kinds of services like driving licenses, energy access, voting, entertainment subscription, and more. To open an account, they will need to demonstrate their identification by engaging individually with each service provider. They will have to recall for authentication purposes the combination of usernames and passwords or other credentials. Decentralized identity management with underlying blockchain and cryptography technologies simplifies the entire process. A decentralized identity environment emphasizes privacy (anonymity) with a login and key management cryptography solution. It not only increases protection and privacy for identity owners but also makes it easier for organizations to authenticate users. Given that the records contained in a distributed ledger are permanent, hackers or unauthorized entities cannot access, steal, or misuse user personal information. Any approved entity requires identity owners' permission to access their Personally Identifiable Information (PII). PII does not reside in the centralized repositories. Each node on the blockchain-based identity network keeps a copy of it on the ledger. It means that there is no risk of a single point of failure. So, a self-sovereign identity based on the decentralized model will protect privacy while ensuring efficiency.
 Also, read | Trust No One: Creating a Blockchain-Based Identity Management System Now, we'll explain how Hyperledger Indy can provide a specific and comprehensive identity management solution for users.
Also, read | Trust No One: Creating a Blockchain-Based Identity Management System Now, we'll explain how Hyperledger Indy can provide a specific and comprehensive identity management solution for users.Identity Management with Hyperledger Indy
The Hyperledger Indy project enables organizations to create a stable, scalable, and flexible solution for self-sovereign identity management. Indy facilitates identification storage at a place where permissioned authorities can change or remove them. Hyperledger Indy platform can list locations with a globally recognizable name once a user provides whereabouts for his identity. When an institution wants to access the identity data, the Indy platform can point out its stored location for verification. Also, read | Blockchain Digital Identity Management | Empowering Individual Data Ownership
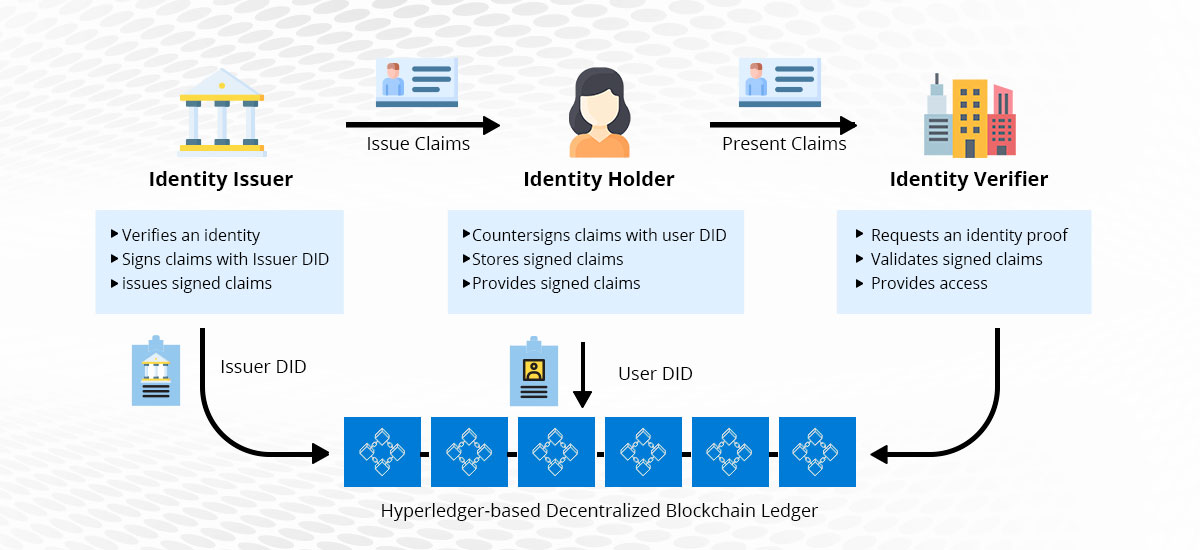
The functions of stakeholders in a self-sovereign identity management system built with Hyperledger Indy are as follows:
Issuer Self-sovereign identity solutions might not depend on having a centralized certificate authority. As per the consent of the identity owner, it can enable a well-defined protocol for establishing, revoking, and exchanging identities. Owner Identity owners have separate identities that are checked by their own set of public/private key pairs. This identity model relies on a decentralized identity management database operated by members of a consortium or network. Validator The identity validator is not a central authority but the trust-gaining parties. Using their private key, they can confirm the identities, while outside parties can check the identity claims with a validator's public key. Users Users of identities use the distributed identity ledger to provide identification and validate them by themselves.
The Process Execution
Users will determine the identity with a human-memorable name. An Indy-based solution can change the identification name into a specific key on the ledger called DID (Decentralized Identifiers). Then, there are primary values called DDO (DID Descriptor Objects). The DDO and DID combination is a DID record. Further, the solution can mark the users on the distributed ledger with a DID record. It uses the private keys of an identity owner to encrypt every single DID record. In the DDO, it creates a public key corresponding to the key-pair with a meta description. DDO also includes a set of service endpoints for communicating with the holder of an identity. There is a specification of the DID system associated with each DID. It specifies the collection of rules for how an institution can report, modify, resolve, and revoke a DID on a particular ledger or network. Control Your Data While it is possible to create a decentralized identity management system using different blockchain technologies, the Hyperledger Indy project aims to develop a solution with the following features: Exchange of verifiable claims controlled by users No question the public Indy network is available to everyone. It is just an identity holder that requires confirmation of the identity. Open provenance for reliable transactions Indy is a centralized platform that offers the sharing of trusted statements with transparent provenance accessibility. Public Ledger Privacy The design of Indy contains a unique feature called privacy by design. Specific concepts of Hyperledger Indy specifically built for decentralized identity enable us to get rid of the current problems in the identity management solution.
Verifiable Claims and Zero-Knowledge Proofs
To prevent unauthorized disclosure of identity attributes, Hyperledger Indy offers built-in support for Zero-knowledge proofs. A verification claim is a condition where the dependent parties need to show details about identity holders. An institution can issue it against unique DID pairs recorded on the ledger, signed by the private key of the issuer, and checked by a public key of an issuer. Off-ledger agents may also use service endpoints discovered in the DDO to manage claim exchanges and verification. For situations where the verification statements deem invalid, Indy provides Zero-knowledge evidence. Zero-knowledge proofs enable identity owners to authenticate the possession of a credential without using anon cred (anonymous credentials) to show the credentials themselves.
Use Case | Exchanging Education Credentials (Claims)
Before the issuance of claims, an educational certificate authority establishes a claim scheme, public keys, and a revocation register as an entry onto the ledger. Further, the authority sends a verification claim to the applicant, confirming that he has completed and passed the graduation via DID A. The applicant then provides evidence of a subset of his assertion to a company where he is applying for a position through DID B, with only specific details he needs to provide. He also offers proof that an identity validator has not removed his claim. Eventually, the organization can check the validity of education certificates without contacting the identification validator. At Oodles, we have a team of blockchain experts of Hyperledger who have a comprehensive understanding of implementing and developing an identity management framework with the Hyperledger Indy.

Our Offices
INDIA
Emaar Digital Greens, Sector 61,
Gurugram, Haryana
122011.
Welldone Tech Park,
Sector 48, Sohna road,
Gurugram, Haryana
122018.















