-
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are continuously seeking innovative solutions to balance transparency, security, and performance. One such innovation that is gaining significant traction is the hybrid blockchain—one of the emerging blockchain development services that converges the strengths of both public and private blockchains into a single, versatile platform. In this blog, we will explore the fundamentals of hybrid blockchains, their technical architecture, benefits, challenges, and use cases. We will also provide actionable insights for enterprises looking to harness this technology to drive digital transformation and competitive advantage.
Introduction
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way data is recorded, secured, and shared across networks. Public blockchains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum have demonstrated the power of decentralization and transparency. On the other hand, private blockchains offer enhanced security, control, and performance for enterprise applications. However, these two models have inherent trade-offs that often force organizations to choose one over the other.
Hybrid blockchains bridge this gap by combining the best attributes of both public and private blockchains. They enable organizations to leverage the immutable and transparent nature of public blockchains while maintaining the privacy and scalability of private networks. This convergence creates a flexible, robust, and adaptable platform suitable for various business applications—from supply chain management and finance to healthcare and digital identity.
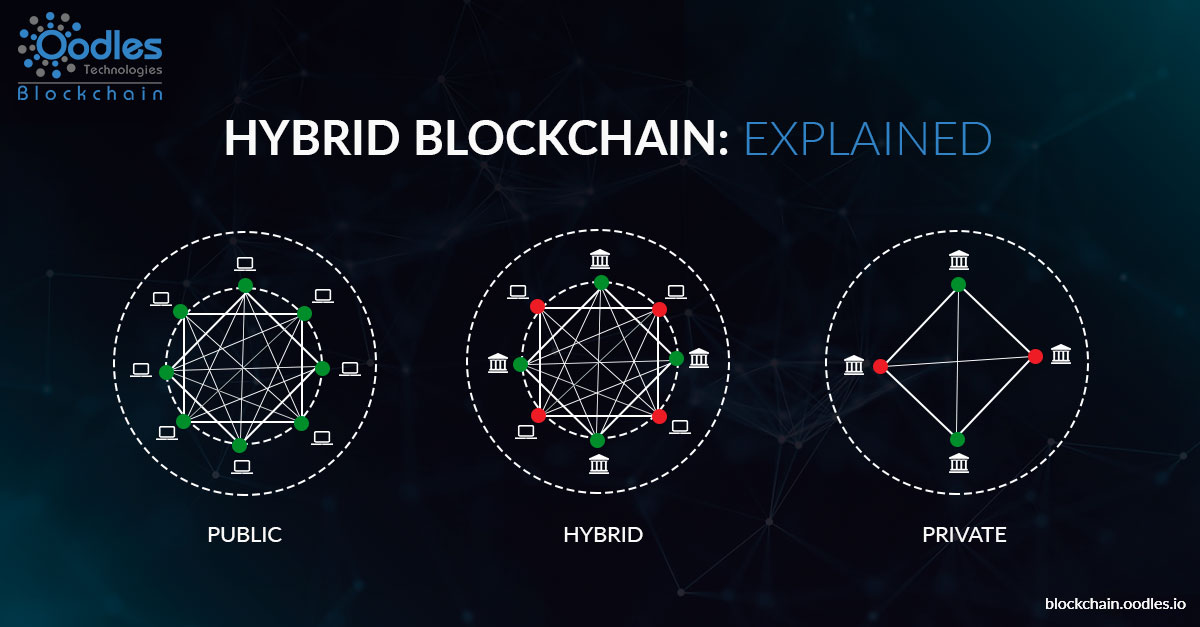
What is a Hybrid Blockchain?
A hybrid blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that integrates the features of both public and private blockchains. It allows an organization to control who can access the network (private aspect) while still benefiting from the decentralization and transparency provided by public blockchains. This duality enables businesses to customize the blockchain environment according to their unique requirements and regulatory landscapes.
Key Characteristics
- Selective Transparency: While sensitive data remains confined within a private network, non-sensitive information can be recorded on a public ledger, ensuring transparency and auditability.
- Controlled Access: Organizations can define permissions and control which participants have access to the blockchain, enhancing data security and privacy.
- Interoperability: Hybrid blockchains often support interoperability between different blockchain networks, facilitating seamless integration with existing systems and cross-chain communications.
- Scalability and Performance: By segregating sensitive operations from public processes, hybrid blockchains can optimize performance and scalability, addressing the limitations often encountered by purely public networks.
Also, Read | The Emergence of Hybrid Crypto Exchange Development
The Convergence of Public and Private Blockchains
Understanding the convergence requires a clear look at the strengths and limitations of both public and private blockchains.
Public Blockchains
Strengths:
- Decentralization: Public blockchains operate on a fully decentralized network, eliminating the need for a central authority.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to the public, which enhances trust and accountability.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data on a public blockchain cannot be altered, ensuring a high level of data integrity.
Limitations:
- Scalability: High transaction volumes can lead to network congestion and slower processing times.
- Energy Consumption: Many public blockchains, particularly those using Proof of Work (PoW), consume significant amounts of energy.
- Limited Privacy: The transparent nature of public blockchains can be a drawback when handling sensitive or confidential information.
Private Blockchains
Strengths:
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Private blockchains restrict access to authorized participants, ensuring sensitive data remains secure.
- High Performance: With fewer nodes and controlled access, private blockchains can achieve higher transaction speeds and efficiency.
- Customization: Organizations can tailor private blockchain protocols to meet specific business needs and regulatory requirements.
Limitations:
- Centralization Risks: With control centralized to a limited group, private blockchains can be more vulnerable to internal manipulation.
- Limited Trust: The absence of a fully decentralized network may reduce the level of trust among external stakeholders.
- Interoperability Issues: Private blockchains may face challenges integrating with other blockchain networks or legacy systems.
How Hybrid Blockchains Bridge the Gap
Hybrid blockchains merge these two paradigms by creating a system where sensitive data is managed privately while public data is shared openly for transparency. This design ensures that enterprises can enjoy the trust and security of decentralized networks without sacrificing the performance and confidentiality that are critical for business operations.
Also, Explore | Getting Started with Hybrid Smart Contract Development
Technical Architecture of Hybrid Blockchains
The architecture of a hybrid blockchain is designed to balance the dual requirements of privacy and transparency. Here, we delve into its key technical components and how they function together.
Dual-Layer Structure
Hybrid blockchains typically consist of two interconnected layers:
Private Layer:
This layer handles sensitive data and business logic. It is accessible only to authorized participants and is optimized for high performance and security. Enterprises can implement complex permission structures, ensuring that only vetted entities can access or modify confidential information.Public Layer:
The public layer is used for operations that require transparency and decentralization. Non-sensitive data, such as audit trails and transaction logs, are recorded here to provide verifiable evidence of activity. This layer leverages the security and immutability of public blockchains, often through mechanisms like digital signatures and cryptographic proofs.Interoperability Protocols
Interoperability is a cornerstone of hybrid blockchains. Advanced protocols and bridging mechanisms allow seamless data exchange between the private and public layers, ensuring that information flows securely and efficiently. These protocols often include:
- APIs and SDKs: Tools that facilitate the integration of hybrid blockchain components with existing enterprise systems.
- Cross-Chain Communication: Mechanisms that enable hybrid blockchains to interact with other blockchain networks, enhancing the overall ecosystem's functionality.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts that automate processes across both private and public layers, ensuring consistent enforcement of rules and policies.
Consensus Mechanisms
Hybrid blockchains may employ a combination of consensus mechanisms tailored to each layer's requirements. For the public layer, proof-of-stake (PoS) or other energy-efficient consensus algorithms are commonly used, ensuring robust security and scalability. In the private layer, consensus can be achieved through more centralized mechanisms that offer faster transaction finality and higher throughput.
Security and Compliance
Hybrid blockchains are designed with robust security features to protect sensitive data while ensuring regulatory compliance. Key security measures include:
- Encryption: Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest, preventing unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Multi-factor authentication, role-based access, and other control mechanisms ensure that only authorized users can interact with the private layer.
- Audit Trails: Comprehensive logging and traceability features are built into the system, enabling real-time monitoring and compliance audits.
Also, Check | A Guide to Understanding Hybrid Crypto Exchange Model
Benefits for Businesses
Hybrid blockchains offer a plethora of advantages for enterprises looking to leverage blockchain technology while maintaining control over sensitive data.
Enhanced Security and Privacy
By segregating sensitive data into a private layer, businesses can protect confidential information from exposure while still benefiting from the transparency of public blockchains. This dual approach significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Improved Scalability and Performance
Hybrid blockchains can handle high transaction volumes by optimizing each layer for its specific purpose. The private layer can be fine-tuned for performance, while the public layer ensures transparency without overwhelming the system. This results in a more responsive and scalable platform that can grow with business needs.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries face stringent regulatory requirements regarding data privacy and security. Hybrid blockchains enable organizations to meet these requirements by keeping sensitive information private and under strict control, while still providing a public audit trail for regulatory reporting.
Cost Efficiency
By reducing the need for extensive computational resources in the public layer and optimizing the private layer for performance, hybrid blockchains can offer a more cost-effective solution compared to purely public blockchain networks. Lower transaction fees and improved efficiency translate to significant operational savings for businesses.
Flexibility and Customization
Hybrid blockchains provide unparalleled flexibility, allowing organizations to tailor the platform to their unique requirements. Whether it's customizing consensus mechanisms, implementing specific access controls, or integrating with legacy systems, hybrid blockchains can be molded to fit a wide range of business applications.
Also, Discover | Types of Blockchain and their Importance in the Digital World
Use Cases and Applications
Hybrid blockchains are versatile and can be applied across various industries. Here are some prominent use cases:
Supply Chain Management
In supply chain applications, hybrid blockchains enable end-to-end tracking of goods while maintaining data privacy for proprietary information. The public layer provides transparency for stakeholders and regulators, while the private layer secures sensitive details like pricing, supplier contracts, and proprietary processes.
Financial Services
Financial institutions can leverage hybrid blockchains to enhance transaction security, reduce fraud, and streamline compliance processes. For example, private transactions such as loan agreements and credit histories can be stored securely on the private layer, while public records of transactions and asset transfers ensure transparency and accountability.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, patient data must be kept confidential, but there is also a need for verifiable audit trails to ensure data integrity and compliance with regulations like HIPAA. Hybrid blockchains allow healthcare providers to securely store sensitive patient information while maintaining a public ledger for treatment records, consent forms, and compliance audits.
Digital Identity Management
Hybrid blockchains offer an ideal solution for digital identity verification systems. Sensitive personal information can be managed within a private layer, while the public layer is used to record and verify identity proofs. This approach helps prevent identity theft and fraud while ensuring that the identity verification process is transparent and trustworthy.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Businesses can integrate hybrid blockchain solutions into their ERP systems to enhance data integrity, streamline operations, and improve supply chain transparency. By leveraging the dual-layer architecture, companies can keep internal processes confidential while providing an immutable audit trail for external stakeholders and auditors.
You may also like | How to Develop a Layer 1 Blockchain
Implementation Strategies
Implementing a hybrid blockchain solution requires careful planning, robust technical expertise, and a clear understanding of business objectives. Here are some key steps for a successful implementation:
Define Objectives and Requirements
Begin by identifying your organization's specific needs. Determine which data and processes require confidentiality and which would benefit from public transparency. Engage with stakeholders across departments to gather detailed requirements.
Choose the Right Technology Stack
Select a blockchain platform that supports hybrid functionality. Evaluate platforms based on scalability, interoperability, security features, and ease of integration with your existing systems. Consider partnering with experienced blockchain development firms if needed.
Design the Architecture
Work with technical experts to design a dual-layer architecture that meets your needs. Define the roles and responsibilities of each layer, select appropriate consensus mechanisms, and establish interoperability protocols between the private and public layers.
Develop and Test the Solution
Leverage agile methodologies to develop the blockchain solution in iterative phases. Begin with a pilot project to test key functionalities, ensure security, and gather feedback. Conduct comprehensive testing, including stress tests and security audits, to validate the system's performance and resilience.
Deploy and Integrate
Once testing is complete, deploy the hybrid blockchain solution in a controlled environment. Integrate with your existing enterprise systems and establish processes for data migration, user onboarding, and ongoing maintenance.
Monitor and Optimize
After deployment, continuously monitor the performance of the hybrid blockchain. Use analytics tools to track transaction speeds, error rates, and security incidents. Be prepared to optimize configurations and update the system as your business needs evolve.
You might be interested in | Unveiling the Potential Layer 3 Blockchain Development
Challenges and Considerations
While hybrid blockchains offer numerous benefits, organizations should also be aware of potential challenges:
- Complexity: The integration of public and private layers can introduce technical complexity. Robust project management and technical expertise are required to ensure smooth implementation.
- Interoperability: Seamless data exchange between layers and other systems can be challenging. Effective use of APIs, SDKs, and standardized protocols is crucial.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory environment for blockchain technology is still evolving. Businesses must stay informed about legal changes and adapt their solutions accordingly.
- Security Risks: While hybrid blockchains enhance security, they are not immune to threats. Continuous monitoring, frequent audits, and comprehensive risk management strategies are essential to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Future Trends
The landscape of hybrid blockchain technology is dynamic, with ongoing advancements that promise to enhance its capabilities further. Some emerging trends include:
- Modular Blockchain Architectures: Future developments may see more modular designs that allow businesses to plug-and-play various blockchain components, enhancing flexibility and reducing implementation time.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: The integration of AI can further enhance blockchain security, optimize consensus mechanisms, and provide predictive analytics for better decision-making.
- Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: As quantum computing evolves, the adoption of quantum-resistant algorithms will become increasingly important to safeguard hybrid blockchains against future threats.
- Greater Interoperability Standards: The development of universal standards for blockchain interoperability will facilitate seamless integration between diverse blockchain networks and traditional IT systems.
Discover more | Layer 0 Blockchain Development | The Foundation of the Future
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is a hybrid blockchain?
A1: A hybrid blockchain is a distributed ledger that combines the features of public and private blockchains. It allows sensitive data to be kept private while leveraging the transparency and decentralization of public networks for non-sensitive information.Q2: How does a hybrid blockchain ensure data privacy and transparency?
A2: Hybrid blockchains use a dual-layer architecture. The private layer stores sensitive data and enforces strict access controls, while the public layer records non-sensitive data, providing an immutable audit trail and ensuring transparency.Q3: What are the key benefits of implementing a hybrid blockchain for enterprise applications?
A3: Hybrid blockchains offer enhanced security and privacy, improved scalability and performance, regulatory compliance, cost efficiency, and the flexibility to customize the platform for specific business needs.Q4: How does a hybrid blockchain facilitate interoperability between different systems?
A4: Through the use of advanced interoperability protocols, APIs, SDKs, and cross-chain communication mechanisms, hybrid blockchains can seamlessly exchange data with other blockchain networks and traditional IT systems.Q5: What industries can benefit most from hybrid blockchain technology?
A5: Industries such as supply chain management, financial services, healthcare, digital identity management, and enterprise resource planning can greatly benefit from the enhanced security, transparency, and scalability provided by hybrid blockchain solutions.Q6: What challenges should businesses be aware of when implementing a hybrid blockchain solution?
A6: Businesses should consider the technical complexity, interoperability issues, evolving regulatory landscape, and the need for continuous security monitoring and risk management.Q7: How can I get started with implementing a hybrid blockchain in my organization?
A7: Start by defining your objectives and requirements, select a technology stack that supports hybrid functionality, design a robust architecture, and work with experienced blockchain developers. Pilot testing and continuous monitoring are essential to ensure a successful implementation.Conclusion
Hybrid blockchains represent a transformative approach to combining the best of both public and private blockchain technologies. By allowing businesses to maintain control over sensitive data while benefiting from the decentralized, transparent nature of public networks, hybrid blockchains offer a versatile and powerful platform for modern enterprise applications.
As organizations navigate the digital transformation journey, the need for secure, scalable, and cost-effective solutions becomes paramount. Hybrid blockchains not only address these needs but also open up new possibilities for innovation in areas such as supply chain management, finance, healthcare, and digital identity.
Implementing a hybrid blockchain requires careful planning, robust technical expertise, and a clear understanding of business objectives. However, the benefits—ranging from enhanced security and regulatory compliance to improved performance and interoperability—make it a compelling choice for enterprises seeking to harness the full potential of blockchain technology.
By embracing hybrid blockchain solutions, businesses can achieve a competitive edge, drive operational efficiencies, and unlock new revenue streams in an increasingly digital and interconnected world. The future of blockchain is not about choosing between public or private—it's about leveraging both to build more resilient, adaptable, and innovative systems.
Note: This article is intended to provide an in-depth technical overview and practical insights into hybrid blockchain technology. For tailored advice and further consultation on implementing hybrid blockchain solutions in your organization, please consider engaging with experienced blockchain experts and specialized blockchain consultants.

Our Offices
INDIA
Emaar Digital Greens, Sector 61,
Gurugram, Haryana
122011.
Welldone Tech Park,
Sector 48, Sohna road,
Gurugram, Haryana
122018.