-
Blockchain first entered our dictionary when cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin appeared in 2008. It is now a system that promises to change entire industries. Business enthusiasts find blockchain equivalent to technologies like AI ( artificial intelligence) or machine learning. Indeed, private and public businesses and government agencies are all working toward using the potential of blockchain technology. Blockchain supply chain development promises accountability in all logistics records and transactions across the freight environment. Ultimately, it leads to optimized supply chain productivity, agility, and growth.
Addressing Logistics Inefficiencies with Blockchain
Essentially stakeholders like shippers, carriers, brokers, and others need to deal with a multitude 'what if' scenarios when sending a truckload of goods across the world. They record each phase of the process with extensive paperwork. The usual operation of transporting goods from producer to consumer is complicated and lacks a common source of truth. Consequently, it makes all involved transactions and constituents traceable.
Particularly, blockchain has the capability of streamlining complex and fragmented processes in the logistics and supply chain industries. It enables the process of documenting transactions immutably and monitoring assets in real-time. Also, its distributed ledger shared across the network creates a transparent and secure mechanism for the management of all logistics documents involved.
Also, read | Simplifying and Augmenting Logistics Processes with Blockchain
Blockchain Workings
Blockchain is a distributed ledger-based technology. It records the entire history of transactions between involved parties digitally. It stores data in "chained" data blocks together. Further, each transaction data block attached to a chain gets stamped with date and time with encryption techniques, rendering it unchangeable. It means nobody can compromise or alter data stored in a blockchain-powered database,
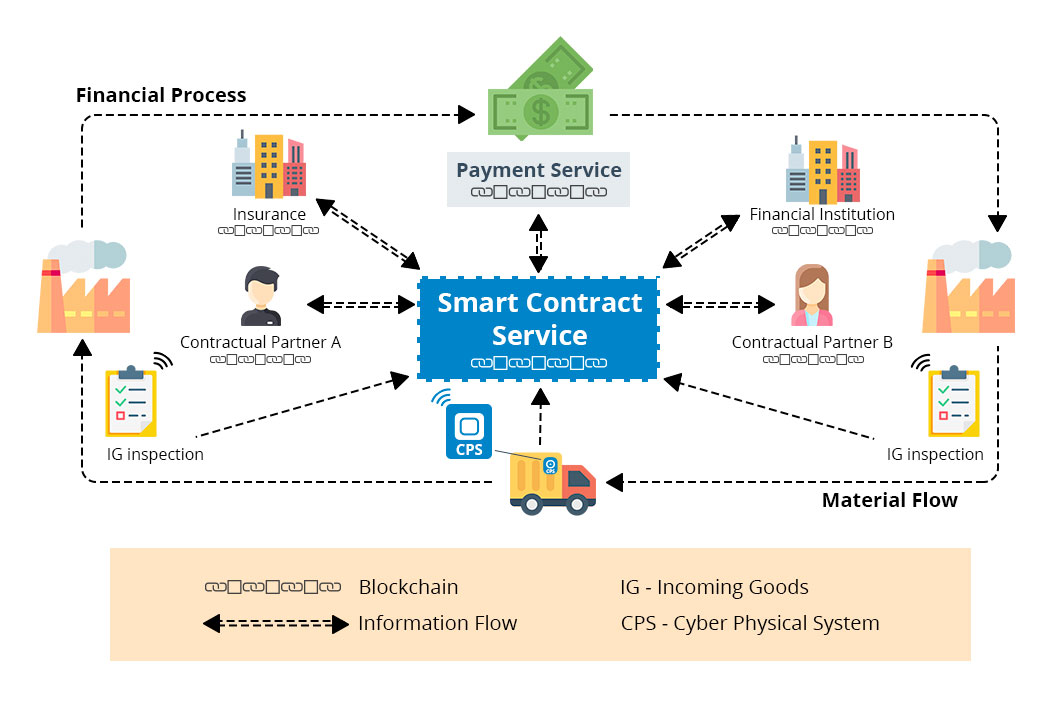
Blockchain technology enables businesses to enforce smart contract solutions — computer coded business contracts or agreements defined between two or more parties and stored on a blockchain. They execute transactions upon meeting terms of an agreement by the involved parties. Numerous parties are involved in the traditional shipping products scenario — shippers, 3PLs, carriers, and consignees. Smart contracts execute transactions for any shipment while storing them on blockchains initiated by these parties, such as BOLs (lading bills), invoices, PODs (delivery proof), and more. Subsequently, each transaction becomes permanently registered on the ledger that any permissioned authority can validate. The network members can use data from a blockchain to verify the block or payload of the transaction, creating a transparent and efficient system for managing all logistics and supply chain documents and transaction information.
Also, read | Making Logistics Processes Efficient with Blockchain Applications
Blockchain in Logistics | Benefits
BiTA (Blockchain in Transport Alliance) has established many immediate benefits of applying blockchain technology in the transport and logistics sector.
Provenance Traceability
Provenance implies any product shipped contains a digital passport confirming its validity. Such so-called digital passports provide crucial details such as when and where the product was made, and what measures it followed during its entire journey.
Smart Contracts
Most find the capacity to issue smart contracts to be the golden standard of blockchain technology. Smart contracts are a big saver of time and resources. "Agreements can be checked, signed, and implemented automatically via a blockchain system with smart contracts."
Fraud Detection
Each transaction occurring on a blockchain is available to everyone on the network. Nobody can erase anything without the system reaching a consensus regarding the change or alteration.
This transparency prevents places where fraud exists, for instance, double brokering. Shippers may securely monitor the time a document or transaction is produced and modified with the standard practice of notarization and non-repudiation, and thus, ensure legitimacy.
Theft Prevention
A blockchain can include specific details and standards, like the photo ID pick-up and delivery specifications. Additional precautions strengthen security, reduce shipment fraud, and enable safe title transfer.
Also, read | German Logistics Managers Resort to Blockchain for New Logistics Systems
Enhanced Payments and Pricing operations
In a blockchain, payment processing and settlement is automated and secure with smart contracts. Also, transaction information is available, providing shippers with more data to set prices.
Quality Assurance
Any approved participant participating in a transaction can access critical data to validate its milestones. The evaluation of freight at pick-up and distribution sites reduces unsubstantiated conflicts.
Real-Time Freight Capacity
Existing capacity in trucking will change by the hour. By openness with blockchain, you'll know when and where resources open.
Monitor Performance History
Tracking carrier and other suppliers' performance history through a blockchain system enables parties to see proof of past success, including on-time deliveries, on-time pick-ups, and more.
Maintain High-Value Assets
It is crucial to provide a trustless and reliable record of product history to ensure it meets the safety requirements from the factory floor to delivery.
Also, read | How Blockchain Transforms Logistics and Supply Chain
Challenges to Widespread Blockchain Adoption
Even after a large number of industries experiencing a positive impact by advancements in blockchain, problems still impact the widespread adoption of the technology. Specific barriers to this are:
Legacy system integration
Organizations should incorporate blockchain technology into their legacy processes, from an ERP to a TMS. Many companies remain hesitant to make a transition to blockchain because of the preparation, time, and resources it requires to be successful.
Ambiguity
Blockchain is modern technology. Although many speak about its prominent potential effect, the influence of blockchain is still unclear, and the market has very few guidelines or industry requirements for implementation and use.
No standardization
To be efficient with blockchain systems, all stakeholders must agree to their data characterizations. Which specifics does every BOL, POD, or invoice contain, for example? And when data is missing or validation, what behavior will trigger?
Cost
It can be costly to build and maintain software and hardware required to operate the blockchain technology. Companies do need technologically qualified people to develop solutions on blockchain technology, which can be a significant expense to them.
Also, read | Streamlining Supply Chain Management with Blockchain Technology
Blockchain Applications in Logistics
While it's hard to predict when the logistics industry will experience wide-ranging blockchain applications adoption, meanwhile you can benefit by participating and looking for opportunities to test projects within the logistics operations and supply chains. However, professionals believe that the development of standards is one aspect essential for the advancement of blockchain technology within every industry. Oodles is one of the leading companies in blockchain technology in developing blockchain applications for the transport and logistics industry. Oodles is actively researching use cases and focusing on creating specific structures and blockchain technologies that can make an innovative impact on the logistics industry.

Our Offices
INDIA
Emaar Digital Greens, Sector 61,
Gurugram, Haryana
122011.
Welldone Tech Park,
Sector 48, Sohna road,
Gurugram, Haryana
122018.